Microbiology and Infection Research Group
The Microbiology and Infection Research Group is interested in understanding the mechanisms and interplay between pathogens and the immune system, as well as identifying novel approaches to prevent and treat infection.
Research Areas
Biofilm research
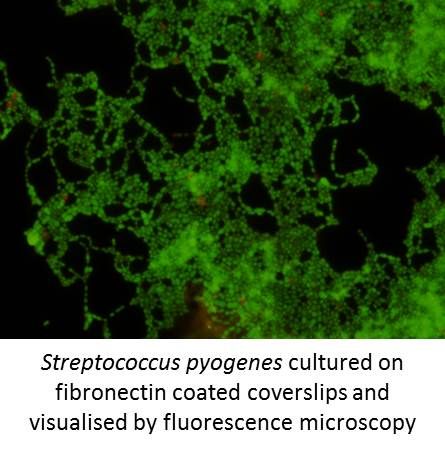 Biofilms are sessile communities of microorganisms which are associated with chronic infections and are difficult to clear by the host immune system or with antibiotics. We utilise a range of static and flow-based methods to evaluate the ability of various pathogens to form biofilms on both biotic and abiotic surfaces. From this we are able to evaluate the efficacy of various compounds to either prevent or remove these resistant entities as well as elucidating their role in infectious disease.
Biofilms are sessile communities of microorganisms which are associated with chronic infections and are difficult to clear by the host immune system or with antibiotics. We utilise a range of static and flow-based methods to evaluate the ability of various pathogens to form biofilms on both biotic and abiotic surfaces. From this we are able to evaluate the efficacy of various compounds to either prevent or remove these resistant entities as well as elucidating their role in infectious disease.
Host-pathogen interactions
In order to understand infectious disease, it is crucial to examine the interplay between pathogens and the host. We utilise a combination of
in vitro cell culture-based methods and
in vivo invertebrate models of infection to study host-pathogen interactions as well as analysing biological molecules directly from clinical samples.
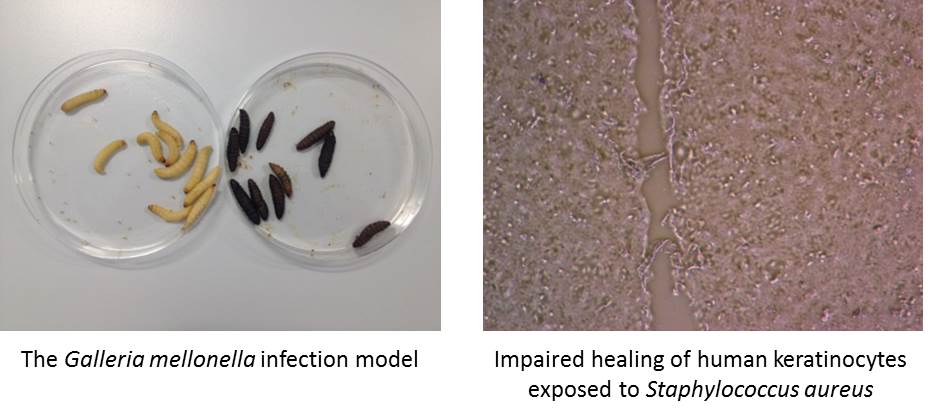
The
Galleria mellonella infection model provides a reliable and inexpensive means to examine the virulence of pathogens, as well as examining the efficacy of novel antimicrobial compounds
in vivo.
G mellonella on the left have received sterile saline, whereas those on the right have received a lethal dose of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Virology
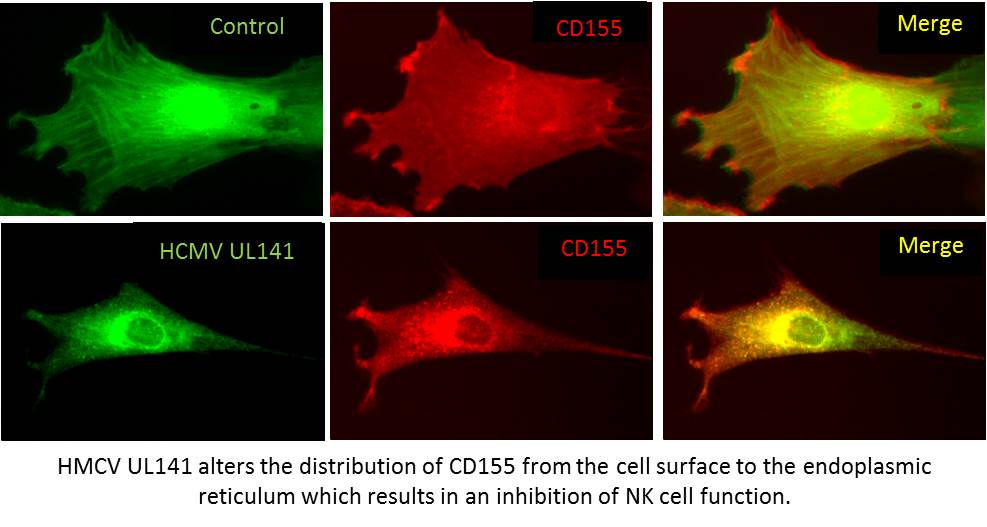
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is a leading cause of illness and death in individuals who have impaired or immature immune systems. It has been known for some time that cells of the immune system, Natural Killer (NK) cells, are particularly important for controlling CMV. However, NK cells are not able to clear CMV from an infected individual. Work by the IRG has shown that this is because CMV is able to evade recognition by NK cells. Our current research is focusing on identifying novel NK immunomodulatory functions encoded by CMV.
Honey as an alternative antimicrobial agent
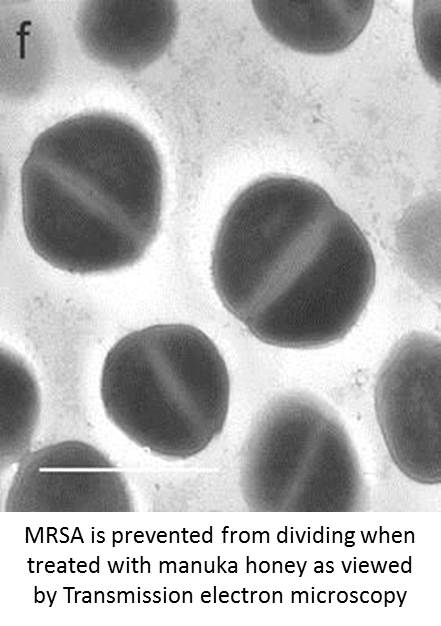 With the continued emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, our research has centred on the evaluation of non-antibiotic agents (including honey and plant extracts) for topical use on wounds. We use both laboratory cultures and clinical samples to study the anitmicrobial effects of novel agents. We have discovered the mechanism by which manuka honey is able to eradicate methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from colonised wounds, which has encouraged clinicians across the world to adopt the use of manuka honey in chronic wound treatment. Our research has also highlighted the potential synergistic effect of manuka honey and antibiotics in inhibiting the growth of MRSA.
With the continued emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, our research has centred on the evaluation of non-antibiotic agents (including honey and plant extracts) for topical use on wounds. We use both laboratory cultures and clinical samples to study the anitmicrobial effects of novel agents. We have discovered the mechanism by which manuka honey is able to eradicate methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from colonised wounds, which has encouraged clinicians across the world to adopt the use of manuka honey in chronic wound treatment. Our research has also highlighted the potential synergistic effect of manuka honey and antibiotics in inhibiting the growth of MRSA.
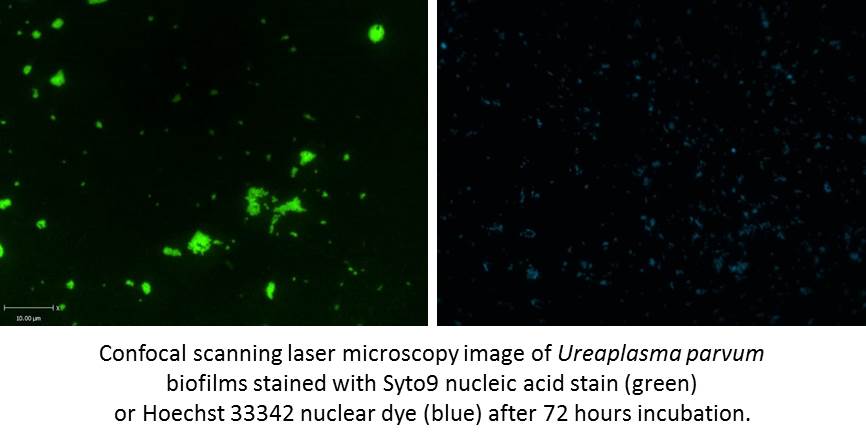
Understanding the role of Ureaplasma species in human health and disease
Ureaplasma species are the most frequently isolated pathogens from placental tissues of females presenting with preterm delivery, and are gaining increased recognition in the field of genitourinary medicine for a role in non-gonococcal urethritis. Our research has been concerned with monitoring levels of antibiotic resistance within patient populations, understanding how colonisation may result in symptomatic disease, and determining the mechanisms by which ureaplasmas are able to evade treatment and the host immune system.
Outreach activities
We are involved in numerous outreach activities which are supported by the Society for Microbiology and the Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) network. Our PhD students run a
Facebook group (Microbiology Wales) that aims to provide young researchers with a forum to discuss microbiology and provides links to resources, training and outreach work.


Group members
 |
 |
 |
Dr Rebecca Aicheler, Senior Lecturer in
Immunology | Lecturer in
Medical Microbiology | Professor Rose Cooper,
Professor of
Microbiology |
 |
 |  |
Lecturer in Biomedical Sciences | Dr Sarah Maddocks,
Lecturer in
Microbiology
| Biomedical Sciences |
 |
 |  |
Academic Associate (PhD) | Miss Jirapon Lueangsakulthai, Academic Associate (PhD, in collaboration with Khon Kaen University, Thailand) | Miss Hajer Taleb, Academic Associate (PhD)
|
Collaborators
Dr Brad Spiller, Cardiff University
Dr Matt Payne, University of Western Australia
Dr Gavin Wilkinson, Cardiff University
Dr Richard Stanton, Cardiff University
Dr Kevin Purdy, University of Warwick
Dr Nicholas Tucker, University of Strathclyde
Dr Robert Atterbury, University of Nottingham
Dr Michael Graz, Neem Biotech
Funding
The IRG is supported by the following:
 |  |  |
|
The Microbiology Society |
Society for Applied Microbiology |
The Royal Society |
 | |  |
| Jane Hodge Foundation | The Waterloo Foundation | KESS2 |
| |  |
Cardiff Metropolitan Research
and Enterprise Services | The Newton Fund | NEEM Biotech |
Key Publications
Beeton ML., Maxwell NC., Chalker VJ., Brown RJ., Aboklaish AF., Spiller OB. ESCMID Study Group for Mycoplasma Infections. Isolation of Separate Ureaplasma Species From Endotracheal Secretions of Twin Patients.
Pediatrics. 2016 Aug; 138 (2).
Stanton RJ., Prod'homme V., Purbhoo MA., Moore M., Aicheler RJ., Heinzmann M., Bailer SM., Haas J., Antrobus R., Weekes MP., Lehner PJ., Vojtesek B., Miners KL., Man S., Wilkie GS., Davison AJ., Wang EC., Tomasec P., Wilkinson GW. HCMV pUL135 remodels the actin cytoskeleton to impair immune recognition of infected cells. Cell Host & Microbe. 2014 Aug; 16 (2): 201-14.
Roberts AE., Maddocks SE., Cooper RA. Manuka honey reduces the motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by suppression of flagella-associated genes. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2015 Mar; 70 (3): 716-25.
Maddocks SE., Jenkins RE., Rowlands RS., Purdy KJ., Cooper RA. Manuka honey inhibits adhesion and invasion of medically important wound bacteria in vitro. Future Microbiology. 2013 Dec; 8 (12): 1523-36.
Jenkins R., Burton N.,
Cooper R. Proteomic and genomic analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) exposed to manuka honey intro demonstrated down-regulation of virulence markers.
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2014 Mar; 69 (3): 603-15.
Cooper R.,
Jenkins R. Binding of two bacterial biofilms to dialkyl carbamoyl chloride (DACC)-coated dressings
in vitro.
Journal of Wound Care. 2016 Feb; 25 (2): 76-82.
